Dr.Harshad Mahatme - Piles Doctor in Nashik
Dr. Harshad Mahatme is a Gastrointestinal Surgeon, Bariatric Surgeon and Piles Doctor in Nashik. has an experience of 13 years in these fields. Dr. Harshad Mahatme practices at Sankalp Speciality Healthcare Private Limited in Tidke Colony, Nashik.
This medical professional is proficient in identifying, diagnosing and treating the various health issues and problems related to the medical field.
This doctor has the requisite knowledge and the expertise not just to address a diverse set of health ailments and conditions but also to prevent them. Because, As a trained medical professional, this doctor is also familiar with the latest advancements in the related field of medicine.
What is pile Surgery?
Hemorrhoids (HEM-uh-roids), also called piles, are swollen veins in your anus and lower rectum, similar to varicose veins. Hemorrhoids have a number of causes, although often the cause is unknown.
They may result from straining during bowel movements or from the increased pressure on these veins during pregnancy. Hemorrhoids may be located inside the rectum (internal hemorrhoids), or they may develop under the skin around the anus (external hemorrhoids).
Hemorrhoids are very common. Nearly three out of four adults will have hemorrhoids from time to time. Sometimes they don’t cause symptoms but at other times they cause itching, discomfort, and bleeding.
Occasionally, a clot may form in hemorrhoid (thrombosed hemorrhoid). These are not dangerous but can be extremely painful and sometimes need to be lanced and drained.
Fortunately, many effective options are available to treat hemorrhoids. Many people can get relief from symptoms with home treatments and lifestyle changes Piles Doctor in Nashik.
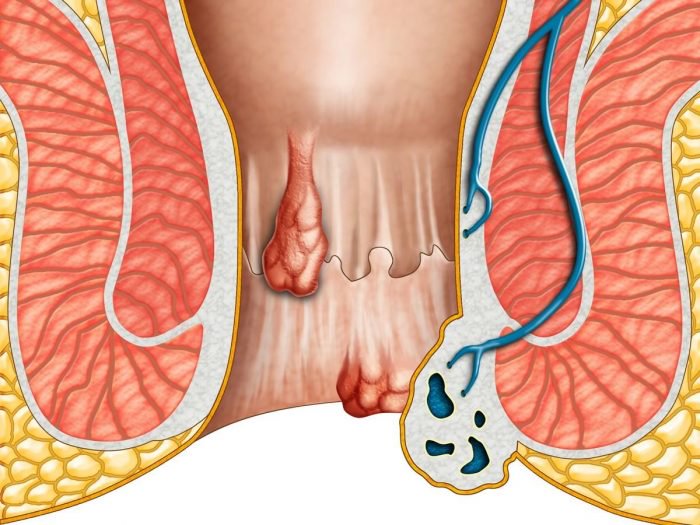
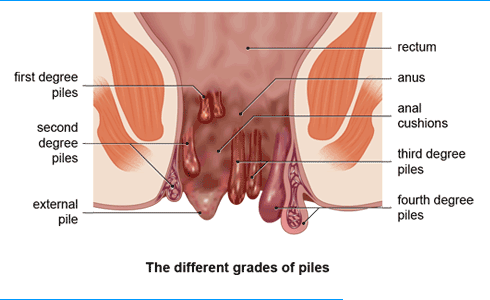
Piles are inflamed and swollen collections of tissue in the anal area. They can have a range of sizes, and they may be internal or external.
Internal piles are normally located between 2 and 4 centimeters (cm) above the opening of the anus, and they are the more common type. External piles occur on the outside edge of the anus.
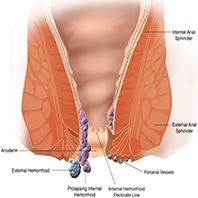
Symptoms of piles
Most cases of piles (hemorrhoids) are mild, and the symptoms often disappear on their own after a few days.
Some people may not even realize they have hemorrhoids, as they do not experience symptoms.
However, when symptoms do occur they may include:
- the bleeding after passing a stool (the blood will be bright red).
- itchiness around your anus (the opening where stools leave the body).
- when a lump hanging down outside of the anus, which may need to be pushed back in after passing a stool.
- In the mucus discharge after passing a stool.
- it may be happiness soreness, redness, and swelling around your anus.
Hemorrhoids are not usually painful unless their blood supply slows down or is interrupted.
Diagnosis
A specialist can usually diagnose piles after taking out a physical examination. They will examine the anus of the person with suspected piles. Tests and methods to diagnose internal hemorrhoids may involve an examination of your anal canal and rectum:
The doctor may ask the following questions:
Do any close relatives have piles?
Has there been any blood or mucus in the stools?
Has there been any recent weight loss?
Have bowel movements changed recently?
What color are the stools?
Causes
The veins around your anus tend to stretch under pressure and may bulge or swell. Swollen veins (hemorrhoids) can develop from increased pressure in the lower rectum due to:
- Straining during bowel movements
- Sitting for long periods of time on the toilet
- Chronic diarrhea or constipation
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Anal intercourse
- Low-fiber diet
Hemorrhoids are more likely with aging because the tissues that support the veins in your rectum and anus can weaken and stretch.
Digital examination. When a digital rectal exam, your doctor injects a gloved, lubricated finger into your rectum. The patient feels for anything unusual, such as growths. The doctor can suggest whether further testing is required.
Visual examination. Because internal hemorrhoids are often too soft to be felt during a rectal exam, your doctor may also examine the lower portion of the colon and rectum with an anoscope, proctoscope or sigmoidoscope.
the doctor may want to examine the entire colon using colonoscopy if signs and symptoms suggest you might have another digestive system disease like colorectal cancer, middle-aged and haven’t had a recent colonoscop
Treatments
Lifestyle changes
A doctor will initially suggest some lifestyle modifications to control piles.
Diet: Piles can happen due to stretching during bowel movements. Extreme straining is the result of constipation. A change in diet can help keep the stools regular and soft. This involves eating extra fiber, such as fruit and vegetables, eating bran-based breakfast grains, increase their water consumption. It is best to avoid caffeine.
Bodyweight: Losing weight may help decrease the frequency and severity of piles. To prevent piles, also advise exercising and avoiding straining to pass stools. Exercising is one of the main therapies for piles.
Medications
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications: These are available over-the-counter or online. Medications include painkillers, ointments, creams, and pads, and it can help relieve redness and swelling around the anus.
Corticosteroids: These can reduce inflammation and pain.
Laxatives: The doctor may guide remedies if a person with piles suffers from an illness. These can help the person pass stools more easily and reduce pressure on the lower colon.
Surgical options
Around 1 in 10 people with piles will finish up requiring surgery.
- Hemorrhoidectomy: The excess tissue that is creating the bleeding is surgically removed. This can be done in various ways and may involve a combination of a local anesthetic and sedation, a spinal anesthetic, or a general anesthetic. This type of surgery is the most effective for completely removing piles, but there is a risk of difficulties, with passing stools, as well as urinary tract infections.
- Hemorrhoid stapling: Blood flow is blocked to the hemorrhoid tissue. This method is usually less painful than hemorrhoidectomy. However, this method can guide to an improved risk of hemorrhoid recurrence and rectal prolapse, in which part of the rectum pushes out of the anus.
